
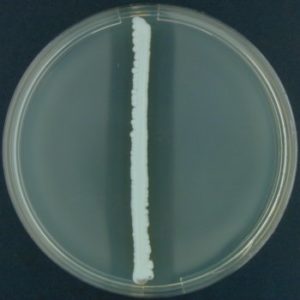
Incubate at 35°-37☌ in ambient air for 48 hours.Inoculate one to two colonies from an 18- to 24-hour culture onto the surface of the slant.If an organism can hydrolyze esculin, the media will turn dark brown or black.īile esculin agar is a selective and differential medium which is used to presumptively identify enterococci and group D streptococci based on the ability of an organism to hydrolyze esculin.īeef extract (11 g), enzymatic digest of gelatin (34.5 g), esculin (1 g), ox bile (2 g), ferric ammonium citrate (0.5 g), agar (15 g), per 1000 mL, pH 6.6. Thus the tolerance to the presence of bile and the hydrolysis of esculin provide the means to presumptively identify organisms. Esculetin reacts with Fe 3+ and forms a dark brown to black precipitate. Organisms capable of growth in the presence of 4% bile and able to hydrolyze esculin to esculetin.

Gram-positive bacteria other than some streptococci and enterococci are inhibited by the bile salts in this medium. Esculetin, in turn, reacts with ferric ions (supplied by the inorganic medium component ferric citrate) to form a black diffusible complex.Bacteria that are bile-esculin positive are able to grow in the presence of bile salts and the hydrolysis of the esculin in the medium results in the formation of glucose and a compound called esculetin.Thus the bile esculin test is based on the ability of certain bacteria, notably the group D streptococci and Enterococcus species, to hydrolyze esculin in the presence of bile (4% bile salts or 40% bile).
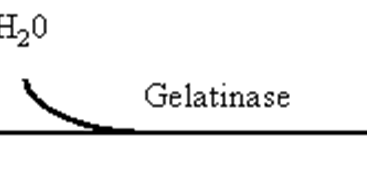
Many bacteria can hydrolyze esculin, but few can do so in the presence of bile.Esculin is a glycosidic coumarin derivative (6-beta-glucoside-7-hydroxy-coumarin). The two moieties of the molecule (glucose and 7-hydroxycoumarin) are linked together by an ester bond through oxygen.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
